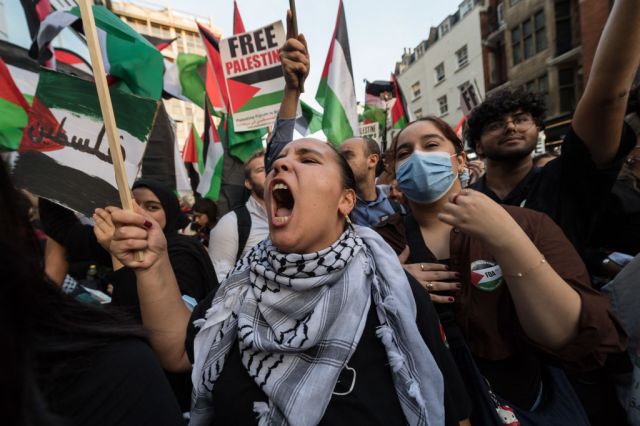
(Wiktor Szymanowicz/Future Publishing/Getty)

Yascha Mounk is one of the foremost critics of the potent new ideology that has swept the globe — variously labelled the social justice movement, “woke” and identity politics. In his new book, The Identity Trap, he takes on this obsession with identity and mounts a defence of liberal individualism and Western humanism as the most effective route to equality and social harmony.
This week, he joined Freddie Sayers at the UnHerd Club to discuss the delusions of the progressive Left, the possibility of a universal politics, and the revival of nationalistic conflict across the world, most recently seen in the attacks on Israel. Below is an edited transcript of the conversation.
Freddie Sayers: What was your initial reaction to the attacks on Israel?
Yascha Mounk: I think one of the things it shows is both what an achievement tolerant, prosperous, liberal societies are, and then, of course, that we mustn’t be naive about what it entails to defend those tolerant and prosperous societies against extremists and theocrats who want to destroy them. Many people have missed the moral implosion of this moment. The Israel-Palestine conflict is incredibly complicated, and I certainly think that Israel is not without its blame, or without its faults in all kinds of ways. But to react to the murder of hundreds of innocent people at a Music Festival, to the kidnapping of an elderly Holocaust survivor and of some toddlers, to the indiscriminate slaughter of civilians with the “both sides” rhetoric that we’ve seen — not just from some parts of the far-Left, but also from many mainstream newspapers, including The New York Times and The Washington Post — is just shameful.
FS: You mean referring to Hamas as “militants” instead of terrorists or talking about how there’s been difficulties on both sides and not taking a clear moral stance?
YM: Yes — there was a really interesting contrast, yesterday evening, where the German newspapers were leading with “Hundreds dead at a music festival” while The New York Times headline was something like, “Israel fights back against militants”. And The Washington Post had “both sides reeling”. After 9/11, many papers around the world, including in Britain, put the faces of 9/11 victims on the front page, and we’ve seen nothing like that in the United States or in Britain. And I think that that is very strange morally. Now, by the way, if Israel goes on to commit atrocities in Gaza, which is certainly imaginable, we should be just as outraged by those atrocities and portray the victims of that as well. But right now, what we have is one of the worst terror attacks we have seen in a long time.
FS: Your new book narrates the rise of identity politics and the loss of that liberal ideal of the state. Taking Israel as an example, it strikes me that it’s a place where there are no universal values that could reasonably apply to both of the country’s communities. And the ideas that you talk about of tolerance and due process, treating people as individuals trying to forget about their ethnicity or tribe, almost aren’t relevant in that kind of context.
YM: I don’t think, right now, there are the preconditions for a great liberal state in which Israelis and Palestinians live side by side. I think that’s naive. But I certainly think that it has universal principles that should be applied. And one of those is what lawyers and philosophers know as jus in bello, the law that governs the conduct of war. Precisely one of the things that I’ve found so shocking over the last days is the failure to distinguish between forms of military action that are targeted at military targets, and that may at times result in civilian loss of life — although you’re trying to minimise that as far as you can — and the deliberate and indiscriminate slaughter of civilians. I think even in situations of war and of conflict, we have certain universal standards of behaviour that we have to try to enforce precisely if we are to stop conflicts from becoming bloodier than they need to be.
FS: What are the preconditions for a liberal society?
YM: Well, one of the preconditions is that you have to be able to see each other as parts of the same polity, parts of the same state. That is what’s absent in the case of Israelis and Palestinians. They don’t have a history as compatriots. And I think it’s unrealistic, given the kind of scenes we’ve seen on Twitter in the last days, that that is going to happen anytime soon. But it’s important when it comes to a place like Britain or the United States. I think one of the key tasks in a deeply ethnically and religiously diverse society is to make sure that people have space where they can have freedom of religion, which is a core liberal value, where there can be freedom of association, where people can continue to be proud of the cultural heritage of origin.
In that way, I’m not anti-identity in the sense that I want everybody in a melting pot pretending they don’t have roots or origins. But at the same time, we need to make sure that they see each other sufficiently as citizens of the same state — as people who might not have certain things in common, but share something else important because they’re both citizens of the United States, or, as you like to say here, subjects of the crown.
Humans throughout history have defined themselves in all kinds of different ways. But then, once you’ve defined yourself as part of the same group, and think of those people over there as part of another group, you’re going to sometimes be capable of great courage and altruism towards members of your group — but you’re also going to treat with disregard, or commit horrific violence against, members of another group. Encouraging young Americans or Britons to think of themselves first and foremost as racial beings — with race trumping any other sense of common identity they might have — sets us up for the worst kind of zero-sum conflict between ethnic groups.
FS: So what is your diagnosis for why issues such as race have come back with such force?
YM: Well, I’ll say two things about that. One is that I think on many metrics, we have continued to improve, certainly in the United States, on race. In the Sixties, less than 5% of Americans thought that interracial marriage was morally acceptable. Now, less than 5% of Americans think that it’s morally unacceptable. And we’ve gone from a vanishingly small number of children having parents of different ethnic groups, to six, seven times more than we did 20 years ago. And that’s just one indication of the ways in which American society has become much more racially fluid. So it’s really a question about the intellectual developments on the Left, based on a fundamental rejection of the kind of universalism that has historically characterised it.
When you go back to the Nineties, all the great internet evangelists had this idea that the thing that’s stopping us from talking to interesting people in Nigeria, or in Japan, is that it’s so expensive to interact. Calling Lagos or Tokyo would have cost you a fortune every minute — and so the idea was that, with costless communication, we’d be able to have a great intercultural exchange. What we’ve found out over the last 30 years is that once you have costless communication, paired with the discovery mechanisms of social media, where you can tag people and things can go viral and so on, what you actually have is people seeking out those who are as much like them as possible. This has revealed something rather sobering about human nature.
FS: How should we fight back against this — you’re a critic of using state power to do so, as is the case in Victor Orbán’s Hungary or Ron DeSantis’s Florida.
YM: Part of our fundamental political settlement is that we have principles that regulate our political competition: that what I’m allowed to say is not decided by Rishi Sunak. At least it should be like that. But in Britain, it’s not always like that. I don’t think that everything is better in America than in Britain, except for the food and the housing and the weather. Many things are better in Britain, but the First Amendment is one of the great things about the United States. And I think we need much more robust protections for free speech here. But that is not just because I care about the great things that come from having free speech. It’s about the terrible things that happen when you don’t have free speech.
And one of those terrible things is that politics becomes an existential battle in which your very ability to make your case and to speak your mind comes to depend on your access to political power. So there’s a very fundamental principle at play here, which is that trying to legislate what you can and can’t say in a university is a fundamental breach of our political settlement. I find it very strange that all of those post-liberals or anti-liberals on the Right and the Left are very naive about how this is going to play out.
On the Left, there are all of these people who are used to just arguing about speech codes at Smith College or Harvard University saying: “We should get rid of free-speech, we should make sure that Silicon Valley companies can censor whatever they want, and perhaps we should have governments being able to persecute you for things that are considered offensive.” But the Left assumes that, even though Britain and the United States are terrible, racist, white supremacist countries, the people who are going to be making those censoring decisions are always miraculously going to be on the side of social justice. That is deeply naive.
So what you actually have is a society that’s completely split, in which, at Smith College, I’m not allowed to talk about this book, and at the University of Florida, people aren’t allowed to criticise free speech or make the case on the other side. And what I want is for the United Kingdom and the United States to have lots of spaces where we can all debate with each other and express our opinions.
FS: Given the depth of the culture war, is it feasible to just say: “Play fair everyone, start getting on and being tolerant with each other, and then everything will go back to normal”?
YM: A lot of the intellectual energy is absolutely on the extremes — so I get what you’re saying. I think people are never liberals in the sense that they have deep down liberal convictions or that they’re able to explain the grand principles of John Stuart Mill particularly well, but I think people especially in Britain have a strong sense of fairness. And I think that sense of fairness is a sense of liberal fairness in that when we do illiberal things — when people get punished for what they say or do in illiberal ways — people are quite horrified by it. On many really important issues, I do think that there is a reasonable majority.
Let me give you two examples: one from the United States, one from the United Kingdom. In America, Democrats think that Republicans don’t want to acknowledge the evil of slavery and Republicans think that Democrats don’t want to acknowledge that George Washington and other Founding Fathers were great men. But a great study by More in Common has shown that that isn’t true. Actually, a huge majority of Americans, including Republicans, want kids to be taught about the evils of slavery, and the huge majority of Americans, including most Democrats, want to be taught about the great achievements of the Founding Fathers. And you can believe both of those things at the same time.
Similarly, the same organisation did a study of opinions about trans issues in the United Kingdom, and you have a clear majority of people in Britain having a lot of compassion for trans people, recognising that trans people have historically been discriminated against in terrible ways, and that we should allow people to live in accordance with the gender identity that they choose. At the same time, the majority have concerns about access to single-sex spaces where biological women are particularly vulnerable. And they reject the idea of athletes who have gone through male puberty being able to take part in female sports at the highest levels. Again, you might agree with some of those views, you might disagree with some of those views. But I think that most citizens are actually capable of making fine distinctions. And we shouldn’t give up on defending that reasonable majority.
FS: What would you make of the suggestion that a lot of the problems from 2016 onwards — the divisions, the populist outrages, etc — have come from an overly naive faith in universalism? That, in fact, there is a tribal element, whether it’s religious or cultural or ethnic, and there are things that do divide us that actually people prefer to stay in touch with. Perhaps people find an overly devout faith in universalism alienating and inhuman?
YM: I like and celebrate the fact that in places like the United Kingdom and the United States, people have origins in different parts of the world and have some ongoing commitment to some of those cultures. And I certainly think that it is naive to be blind to the power of those collective instincts. Human beings are group-ish creatures. We have a tendency to think in groups and to prioritise the members of in-group over the out-group. Perhaps your criticism would be fair if you were addressing the 20-year-old version of me, who believed that we should get over patriotism and nationalism, and all those kinds of things and feel equal duties and regard for everybody in the world. I still find that sort of charming ideal, but in reality, we’ve seen over the last 20 or 30 years that nationalism is a very powerful force.
FS: So where does that put you on an issue like immigration? Take Sweden: two million out of the 10 million citizens of Sweden are new arrivals, in that they came in the past 10 years. Many of them are from Somalia, Syria, Egypt, and Turkey. And it certainly feels to a large minority of Swedish voters, who are now voting for quite radical parties, that inviting that volume of people in was precisely a kind of overly universalist ideal that has not worked out and has really damaged the country.
YM: I don’t think that any form of liberal philosophy necessitates open borders. And I think it’s absurd to think that it does. On immigration, my sense is that the great majority of citizens in virtually every country understandably want their nation to have clear control of its borders, and to be able to decide who gets to come in, and to make sure that the people who come in don’t present a danger and that they share some of the basic values of that society. And then we can have debates about what the right level of immigration is. And that’s going to depend in many cases on local circumstances of all sorts.
I think what’s interesting is that once you have very clear control of a border, a lot of people see the benefits of a healthy level of immigration, particularly when those people are highly skilled, and already speak some of the language of the country they’re immigrating to and so on. But I certainly don’t think that wanting to have control of your border is in any way irreconcilable with the principles of liberalism, and I don’t think any serious liberal philosopher in the history of the liberal tradition has claimed that.
FS: So the book is making a “yes, but” case for that universal ideal?
YM: The ideology that I’m analysing has three main claims. Number one, that the key prism for understanding social reality, for understanding our conversation today, for understanding history and political events is race, gender and sexual orientation. That is the key prism, you should always focus on. Somebody like Robin D’Angelo, a very influential diversity trainer and bestselling author, has argued that every time a white person interrupts a black person, they’re bringing the entire power of white supremacy to them. That might be true in certain circumstances. But there’s going to be lots of other circumstances where that’s not true.
The second claim they make is that the values in the unwritten constitution settlement in Britain, the values written down in the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution of the United States, aren’t what allowed us to make progress towards more just societies, historically. They were meant to pull the wool over our eyes. They were meant to perpetuate injustices like racism, and sexism. They’re the real reasons why our societies remain unjust today. And so therefore, we should reject any form of universal value, neutral rule, including free speech, by making how we treat each other and how the state treats all of us explicitly depend on the kind of group of which we’re from.
So what is a defence of universalism? It is to counter each of those points. And liberals can do that very convincingly. It is to say number one, but of course, race and gender and sexual orientation matter. But so does social class. So does religion. So do the individual tastes and attributes of people, you have to let each situation teach you how to read it, not impose a pre-existing view on it. But number two, those universal values is how the gay rights movement succeeded, how the Civil Rights Movement succeeded. Frederick Douglass, recognising that free speech allowed people to say terribly racist things in his day, called free speech, the “dread of tyrants”, because he realised it’s also what allowed the weakest in society to make their case for more equal rights. Therefore, the way that we make progress is to recognise where we’re hypocritical, recognise where we’re not living up to our ideals, but also to double down on the goal of living up to those universal values and neutral rules, rather than ripping them up.
FS: I think now is a great moment to take questions.
* * *
Question One: Is identity politics filling the vacuum caused by the decline of class politics?
YM: You start seeing the rise of many of these identity-based Left-wing movements in the Sixties, Seventies and Eighties; they carve out a little niche for themselves, but they’re clearly minoritarian traditions. It’s only after 1989 — when Marxism and class-based politics really loses legitimacy that always came from communist regimes in the East — that that could become the majority tradition. That’s one part of it. I think there’s a parallel question about the role of religion, and whether cancel culture is filling a religion-shaped hole, especially in the United States.
Europeans tend to think of America as a Puritan place in certain ways. And sometimes we think that’s because there’s a Bible Belt and half of Americans say they’re not going to have sex before marriage. But really, I think that the inheritance of Puritanism is about the moral imaginary, which is as strong today among the highly educated progressive Left in Boston as it is among poor people in Ohio. They’ve given up the moral precepts of Puritanism, but the desire to maintain a morally pure community, the instinct towards self-flagellation, and of course, the instinct towards purifying the community by casting any suspect people out of it remains very deeply shaped by that.
Question Two: It seems to me that the culture wars are a result of a decline in or a destruction of trust in institutions across the Right and the Left. I think the only thing which unifies all the different factions is that none of them trust institutions anymore, which to me is much more of an existential threat than the culture wars themselves. It would be really good to hear your views on that.
YM: I half agree with that. I worry a lot about the loss of trust in institutions. You need functioning institutions, and you need some amount of trust in them for us to be able to solve basic problems and have elections to decide who should be in power, which is something we can’t take for granted any more in the United States. But the problem, of course, is that the presence of some genuinely stupid ideas in these mainstream institutions is part of what has driven the lack of trust in them. And so, I sometimes get the sense that my friends and colleagues want to tell me, “Look, it’s really important that people trust these institutions so let’s shut up about when they screw up.” And I think there’s a strain of journalists, who say, “If only we frame things in the right way, we can hold the shop together.”
Speaking as somebody who is deeply concerned about the threat of certain forms of Right-wing and Left-wing populism to our democratic institutions, a lot of journalists have started to write stories with an eye to how to save our democratic institutions and make sure that Donald Trump is not re-elected in 2024. But it turns out that doing that is actually a really bad way of defending democracy because people aren’t stupid and they recognise that that’s what you’re doing. And so in the same way, we need to figure out how to increase trust in our institutions. But the first step towards that is to argue back loudly and proudly against the bad ideas that now have purchase in these institutions, rather than to shut up about those bad ideas because we’re fearful that talking about this might somehow make people recognise that something’s going wrong.
Question Three: Could you expand a little bit more on the interplay between identity politics and people seeking power through it, political power, and whether that is a deliberate mechanism for undermining what you might call the liberal centre?
YM: Let’s distinguish two things: the ideology opposed to liberalism and the motivations of the people who engage in this form of politics. On the first question, this is an explicitly anti-liberal tradition. That’s a really important thing to recognise. Critical race theory has become really abused term because some people on the Right say, “It’s critical race theory if you want to say a negative word about the Empire,” or about teaching kids about slavery in American context. As a result, a lot of the mainstream has said, “Well critical race theory, that’s just wanting to think critically about the role that race plays in society. What could be wrong about that?”
And of course, race does play a significant role in our society and inspires genuine injustices and we should absolutely be clear and explicit about that. But when you go back to the thought of the founders of critical race theory, such as Derrick Bell and Kimberlé Crenshaw, you recognise how explicitly they think of liberals as the enemy — more than conservatives. Derrick Bell, who did heroic work helping to desegregate and integrate schools and businesses and other institutions throughout the American South in the Sixties, comes to think of that work in many ways as a mistake. He comes to agree with segregationist Southern senators who said that civil rights lawyers were just trying to impose their integrationist ideals and don’t really care about their clients. That’s why his first paper is called “Serving Two Masters”: they claim to serve the clients but they’re actually serving that ideology.
And so he says, we need to reject, “the defunct racial equality ideology of the civil rights movement”. Once you get to somebody like Kimberlé Crenshaw, she explicitly says that the basic ideas of Barack Obama are fundamentally at odds with the core assumptions of critical race theory. So intellectually, this is a tradition that is founded on the rejection of Martin Luther King Jr and in some ways of Obama, and Frederick Douglass, and really the core thinkers that have dominated African-American political thought. Now, I think the motivations of people who engage in this kind of politics vary hugely from person to person. I think there are some people who are abusing this politics as an excuse to bully and to punish. And that is in general true in the political extremes: they have a surfeit of people with what psychologists call a “dark personality triad”. And that’s part of the phenomenon.
But there are also a lot of people who are attracted to these ideas for reasons that are understandable. There are many injustices that they’re genuinely horrified by, and perhaps don’t have the historical perspective to recognise the ways in which we’ve made progress. And they genuinely believe that implementing these ideas is going to lead to a better world. And that’s why I think we should argue back, claiming the moral high ground in good faith. Because these are people who are persuadable.
Question Four: It’s often said that postmodern philosophers like Jacques Derrida write impenetrable gibberish — not so much bad ideas, just a bad combinations of words. And, if we do anything well in this country, it’s satire and mockery, just actually saying, “Those words in that order don’t make sense”. Is it worth just pointing out the aspect of this that is just lazy writing?
YM: In the intellectual history I tell at the beginning of the book, I was struck by the fact that the theorist that ended up being most influential, by and large, were not very obscure. So I think Gayatri Chakravorty Spivak is the one person in this pantheon of influences I chronicle that is very hard and not fun to read. And she came up with this idea of strategic essentialism. It ends up being really influential but you go back to the text and read it, you think, “How could that influence anybody?’” But Edward Said and Derek Bell and Kimberlé Crenshaw are very clear writers. Michel Foucault is kind of a little hard to read in certain ways, but also has a real rhetorical power and this is in certain ways a pleasure to read.
The sort of literary theory that really is incomprehensible post-structuralist gobbledygook is not part of the set of thinkers that really ended up influencing this. But the use of humour is really important, and Spivak is the one person I genuinely suffered through as I was researching this book, because her writing is so terrible. She recognised that herself as well. And one of the interesting little subplots is how Said and Spivak and I think Foucault did or would have come to criticise what became of their ideas, and the way that Spivak did this too. She has origins in India and with reference to the chaiiwalas, who sell tea in the streets of India, she complained about the humourlessness of the identitywalas at American universities.
Question Five: If these ideas have captured academia, captured HR, captured the corporate world and you do not have a mainstream political party to vote for that looks anything like your classical liberalism, what are we going to do about it? A moral crusade, a new political party, changing the voting system?
YM: How did those ideas win? Not with a new political party, not with some grand new law or anything like that but through public debate, through influencing how people think, and through gaining a kind of — ironically, this is a postmodern concept — discursive hegemony. And so how do we change that, again? By convincing people and speaking up and winning the argument. Most people don’t have very strongly held beliefs. They’re going along with whatever they think is the sensible thing to say, whatever the consensus of their colleagues seems to be. But that means that you can change what that set of ideas and norms is by making some noise.
I do think that we’re starting to see a little bit of pushback in important ways. One example is Ibram X. Kendi, one of most effective popularisers of these ideas, and one of the less sophisticated ones. He was beyond criticism in the United States over the last three years. I know of many friends who had stories, criticising the content of his views or reporting on some of the things he’s been doing at a centre in Boston University, whose stories were killed. Well, suddenly, the dam broke, because he fired a lot of his staff. And it turned out that he had promised all kinds of things that he would do with his grants that he never delivered on and so on.
Suddenly, everybody’s saying what they have been quietly thinking for three years. And that’s genuinely changed the tenor of the conversation. So now I often have people come to me and say, “Look, I want to argue back against this, but I’m so worried about cancel culture and what’s going to happen to me,” and I understand those concerns. I’ve reported on some of the people who’ve been fired for absolutely ridiculous absurd things. I understand why people are worried about it. But I think it’s important for us not to exaggerate the hold of those mechanisms, the hold of those ideas. Because once we start speaking up, we’re actually in the majority.
And because I think if you make it clear that you’re not nervous about pushing back, and you don’t have to behave like a jerk, you demonstrate that you’re motivated by your own vision for how to make society a better place, in most contexts, you can speak up, you can criticise, you can defend these liberal values. And if we all start to do that, I think that’ll make a difference. So I guess I am very worried about the way in which I think over the next 20 years we’re going to have a society-level confrontation over these ideas and the influence they will have. But I think that’s a winnable debate.








Join the discussion
Join like minded readers that support our journalism by becoming a paid subscriber
To join the discussion in the comments, become a paid subscriber.
Join like minded readers that support our journalism, read unlimited articles and enjoy other subscriber-only benefits.
Subscribe