ME/CFS sufferers have felt abandoned for years

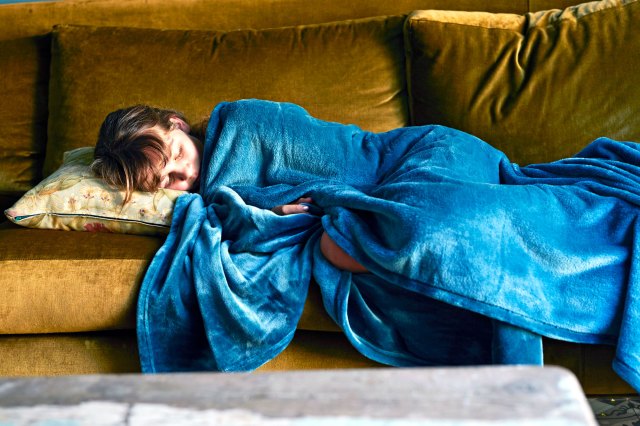
There is surely no disease more cruelly misnamed than “chronic fatigue syndrome”. It is mysterious, apparently triggered by viral infection, and can last for months, decades, even a lifetime. Patients can be housebound or even bedbound for years. But the name makes it sound like they are just a little bit tired.
Apart from Covid, it is probably the most controversial disease in the world and, in fact, chronic fatigue, or ME/CFS to give it its proper name, does seem to share many features and symptoms with “long Covid”: fatigue, brain fog, pain on exertion, the assertion that the affliction is purely psychological. And for over three decades, patients have been told that the treatment for it is to get up and do some exercise, even though for many, exercise seemed to actively make their condition worse. They have been told, in near-explicit terms, that it’s their responsibility to get better.
Recently, it looked as though that was going to change. The NHS guidelines for treatment were going to be updated, and patient groups were happy. But then, at the last minute, that was delayed, and many patients are feeling betrayed and furious. One man I spoke to, John Peters, has been in its grip for 35 years.
For John, formerly “the fittest man in his rugby team”, the main symptoms were cognitive. He struggled to remember things, or recognise faces. He walked past his own sister in the street; he once enthusiastically shook the hand of a stranger, thinking he was his cousin. But there was also psychic pain: an “electric storm in my head”. He’d get up at 1pm and go to bed at 10pm but not sleep, just have hallucinatory fever-dream “white nights” and be in tears at 6am begging for sleep to come.
John’s case is typical of many. The disease onset is often linked to a viral infection: patients recover from that, but then something goes wrong. Some recover in a few months. Others never do. And no one knows what causes it.
Hence the excitement last week about the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) new guidelines for treatment. And hence the rage when the publication was delayed.
All those many patients — between 130,000 and 260,000 at the last count — who have felt ignored and belittled, or that they were being blamed for their own failure to recover, thought that, at last, their concerns were being taken seriously. Now that it has been kicked into the long grass, they are furious.
To understand the rage, it’s useful to understand the trouble with the currently disputed NHS-approved method for treating ME/CFS: a combination of cognitive behavioural therapy, CBT, and “graded exercise therapy”, GET. The approach is based on a theoretical model of how the disease works called the “biopsychosocial model”.
The basic idea is, first: someone gets ill with some virus. A cold, the flu, whatever. While they have that virus, they become deconditioned. So when they next try to do their normal level of exercise, it hurts, and they feel exhausted. The patients attribute that to the disease, and stop doing exercise. So they become even more deconditioned, and so the next time they try exercise, it becomes even more painful and exhausting. It becomes a positive feedback loop – the pain prevents the exercise, and the lack of exercise increases the pain.
This model was first really applied to ME/CFS in a 1989 paper: it represents, according to the authors, “a transfer of responsibility from the doctor, in terms of his duty to diagnose, to the patient, confirming his or her duty to participate in the process of rehabilitation”. Understandably enough, patients took this to mean that getting better is their responsibility, and if they don’t it’s because they haven’t worked hard enough.
The associated treatment involves a steady (“graded”) increase in exercise, and “cognitive work to break the association between increase in symptoms and stopping or avoiding the activity”.
Again: to many patients, this very much sounded like being told that their condition was their own fault. Your beliefs that you are ill are in fact causing you to be ill. And it didn’t match with their experience of the disease, and specifically something called “post-exertional malaise” – that is, huge flare-ups of the condition caused by exercise.
But it doesn’t matter whether patients didn’t like this model. What matters is whether it is a useful one, and whether the CBT/GET treatment works.
When the 1989 paper was written, there was no evidence for the model; it was purely hypothetical. In 2011, though, that seemed to change. The PACE trial looked at CBT/GET treatment for ME/CFS. It gave about 600 patients either normal medical care, or normal medical care plus CBT/GET. Then it asked those patients to fill out forms reporting how fatigued they felt and how well they were able to function physically. People who had had CBT/GET reported greater improvement than the ones who had only had standard medical care.
But patients’ groups were unimpressed with the study, and so were some other researchers. Jonathan Edwards, a professor emeritus of connective tissue medicine at UCL who has been a critic of PACE since its publication, told me that the problem is that PACE is unblinded, and uses subjective outcomes.
In the best research, subjects are “blinded”: they don’t know whether they’re getting the real treatment or a placebo. It stops the trial being biased by patient expectations. But sometimes you can’t do that, so it’s important to use an objective outcome. For instance, if you’re measuring the impact of a drug on your blood potassium levels, then it might not matter if the trial isn’t blinded, because patients’ expectations probably won’t affect their blood potassium. But you need to do one or other, either blinding or objective measures (and ideally both).
The PACE trial, though, took a subjective outcome – patients’ self-reported physical activity and fatigue – and an unblinded population, and so was at risk of patients simply telling researchers what they obviously wanted to hear.
You absolutely can get quite large effects like this, says Edwards. He refers in his evidence to NICE to a study into a drug, rituximab, in treating ME/CFS. It found an apparently strong effect – but it, too, was unblinded and subjective. And a follow-up study, with rigorous blinding, found nothing. It didn’t work any better than placebo.
Over the last four years, NICE has been reassessing the evidence, partly as a result of patient pressure. They looked at the PACE trial and several other more recent ones into CBT/GET. For both elements – the CBT and the GET – the experts who looked at it concluded that the evidence “ranged from low to very low quality”, mainly for the reasons described above.
That assessment was made public as part of a set of draft guidelines published in December last year. The new guidelines said that clinicians should no longer offer ME/CFS patients “any programme based on fixed incremental increases in physical activity or exercise, for example graded exercise therapy” and to only offer CBT as support for managing their symptoms, not to offer it as a treatment for ME/CFS itself.
Then, the day before the final guidelines were to be published last week, came the announcement that they were to be delayed. Clinical bodies, including the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health (RCPCH) and the Royal College of Physicians (RCP), put out statements welcoming the pause.
But no one seems to want to say why. For instance, Trudie Chalder, one of the authors of the original 1989 paper, gave a quote welcoming the delay because the new guidelines were “confused”. But when I asked her about it, she said she couldn’t comment until the new guidelines were published, which was odd, since she already had. “I can’t be more specific at this time,” she said when I followed up. “I think it’s better to wait until we see the final guidelines.” NICE themselves wouldn’t talk to me except to point me to their statement.
The RCPCH didn’t want to say anything except that they hope “our evidence and other people’s will be made public in good time”.
The only hint of what has gone on seems to come from Dr Andrew Goddard of the RCP, who said “We were extremely concerned that the final guidelines proposed by NICE may not have taken into consideration the extensive comments we made to the draft version.” It seems likely that NICE has delayed its publication because, basically, clinicians’ groups were angry that their preferred method of treatment has been dropped.
This isn’t how NICE is supposed to operate. NICE is supposed to take into account the clinicians’ submissions, of course, but not to be beholden to them. Chris Ponting, a professor of human genetics at Edinburgh University, told me that “The NICE panel was put together from all walks of life; highly respected individuals esteemed in their individual areas. They thought that all of the evidence [for CBT/GET] was of low or very low quality.”
“I’ve seen on social media that this is a political process because there is a veto given to certain groups,” Ponting added. “I really hope that these claims are wrong, and that these guidelines are published without any further delay. If NICE are bending to some professional lobby now, would they also bend to pharma companies?”
I am genuinely confused by this: NICE has, since its founding, been one of the best things about the British healthcare system. It has been scrupulous at establishing which treatments are cost-effective and which are not, often in the face of severe public and media pressure. So it’s really important to find out what’s happened here: the full publication of the guidelines, and of all the submitted evidence, would be a good starting point.
Researchers have defended the PACE trial by saying that it is difficult to do good blinding and use objective measures in things like ME/CFS. And the infectious disease physician Andrew Miller, in defence of the treatment, says that “without CBT and GET, there is nothing. No new therapies or approaches have emerged since 2007 [when the current guidelines were established].”
But the fact that it’s hard to get good evidence doesn’t make the evidence you have better. And the fact that there aren’t well-evidenced therapies doesn’t make the therapy you have better-evidenced. Science isn’t graded on a curve: “If results are unreliable, they cannot be considered reliable just because it is difficult to get more reliable ones,” as Edwards put it in his evidence to NICE (his emphasis).
Meanwhile, a fraught area of medicine gets even more toxic. When I last wrote about ME/CFS, in 2017, one researcher told me that “The last time I said anything public about CFS, I got followed around by an angry mob for about a year, on Twitter and email. Some even turned up to talks I gave, and I’ve heard of them turning up to people’s houses or doxxing them.” The author of a study in that piece said she had received death threats. Another researcher, who I know personally to be pretty fearless, told me when I tried to speak to them for this piece: “I’m afraid I don’t go within a million miles of ME/CFS these days. Just too much grief.” ME/CFS patients have a reputation for being angry.
Partly I think that’s caused by the sheer number of patients – approaching a quarter of a million in the UK alone. With that number of people, it only takes a tiny percentage to contaminate the whole debate. But it’s also because those people have felt ignored for so long.
Often the argument between sufferers and observers descends into a poisonous row over whether ME/CFS is “psychological” or “physical”. But patients like John are keen to stress that that shouldn’t be the area of contention. What’s important is that the CBT/GET paradigm doesn’t seem to work, at least beyond a placebo effect in a subset of patients. The evidence has been assessed and found wanting and the delay in publishing the guidelines just means that more patients will be put through it, against what appears to be the best scientific evidence.
So NICE must swiftly publish their new guidelines along with all the evidence from the patients’ groups and professional bodies attached. They should explain this delay, beyond the boilerplate statement, because as it stands it looks awfully like its decision-making process has subverted. And, they should trigger some more real research into the causes and nature of the disease. Perhaps the rise of long Covid will help encourage that. Otherwise more lives will be lived in a cruel twilight, like John’s, 35 years after diagnosis: “I’m 60 now. I have nothing, I have no one. I have no memories; my life is unlived.”








Join the discussion
Join like minded readers that support our journalism by becoming a paid subscriber
To join the discussion in the comments, become a paid subscriber.
Join like minded readers that support our journalism, read unlimited articles and enjoy other subscriber-only benefits.
Subscribe