
Having spent the past month traveling around the United States — from major cities to the countryside — the scale of the ‘movement’ which erupted in late May after the death of George Floyd is almost incomprehensible. According to the New York Times, which relays their finding with obvious excitement, the ‘movement’ (its precise contours seldom defined) “may be the largest” in U.S. history.
That is certainly plausible. In which case, it would presumably be important to document how ordinary Americans, especially those most directly affected, perceive the “movement” in question.
Scan almost any of the popular media coverage over the past six weeks and you’ll find that journalists have been steadfast in their depiction of “protesters” as unassailably “peaceful.” While the vast majority of those who attended a state-backed demonstration or some other event spurred by the ‘movement’ are unlikely to have committed any acts of physical destruction, the term “peaceful protest” doesn’t seem to quite capture the impact of a society-wide upheaval that included, as a key component, mass riots — the magnitude of which have not been seen in the U.S. since at least the 1960s.
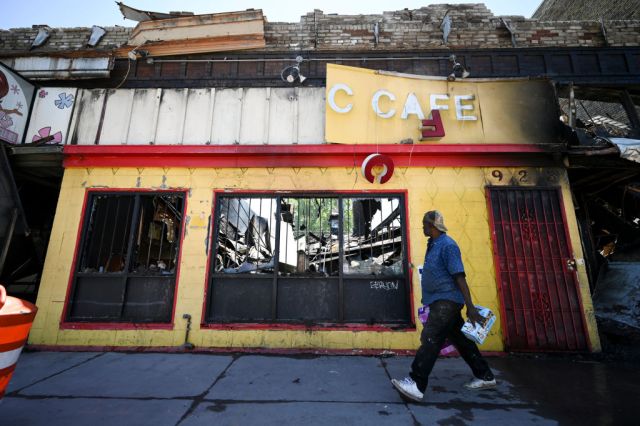
From large metro areas like Chicago and Minneapolis/St. Paul, to small and mid-sized cities like Fort Wayne, Indiana and Green Bay, Wisconsin, the number of boarded up, damaged or destroyed buildings I have personally observed — commercial, civic, and residential — is staggering. Keeping exact count is impossible. One might think that a major media organisation such as the New York Times would use some of their galactic journalistic resources to tally up the wreckage for posterity. But roughly six weeks later, and such a tally is still nowhere to be found.
A standard retort one often hears is that “the riots” must not be conflated with “the protests,” which is technically accurate in certain contexts. But the distinction is not as obvious as the media like to make out. In many locations, police and fire services were diverted to accommodate these massive protests, which in turn created a vacuum that enabled the outbreak of riotous activity. As one resident of Minneapolis explained to me, emergency services told him that they would simply be unavailable during the weekend of 29-31 May, while other locals recounted with amazement that police were totally absent as their neighbourhoods burned.
In Milwaukee, a man described being chased down by rioters after getting off the bus on his way home from work. He saw no difference between protesters and rioters; the flippant idea that these groups can be so neatly disentangled is wrong.
This view is just as likely to be espoused by black people and other minorities as anyone else (the Milwaukee man was black), which renders the media’s strident insistence to depict the ‘movement’ as entirely peaceful incongruous with the perceptions of working-class Americans (of all races). So many of them experienced what transpired more as a painful tragedy than any kind of wondrous harmony.
Indeed, the resulting destruction may have set their majority-minority neighbourhoods back economically for months or years, if not longer. Most had already been struggling due to the pandemic, with the riots interrupting fragile reopening plans. To exclude the perspectives of these people from popular media narratives amounts to a kind of purposefully obfuscatory, moralising snobbery. Talk about ‘erasure’.
So why, exactly, has the scope of these riots been so assiduously downplayed, and the opinions of those who experienced them first-hand been largely ignored? A number of potential explanations ring true. For one, media elites desperately do not want to undermine the moral legitimacy of a ‘movement’ that they have cast as presumptively righteous. And highlighting that urban minority populations are generally less enthusiastic about a movement whose mantra is “Black Lives Matter” would be embarrassing for obvious reasons.
The white liberals and Leftists who claim to be so sensitively attuned to the feelings of minorities clearly spend very little time actually talking to working class non-white people — or at least those who happen to fall outside their activist cohort. If they did, they would be saddened to discover that, unlike them, working class non-whites frequently express “small-c” conservative cultural attitudes.
For instance, black Americans whom I’ve spoken to on the street across America in randomly-selected encounters were almost unanimous in their approval of the National Guard deployments to their neighborhood during the riots. If anything, their main criticism was that these deployments came too late to prevent the destruction.
This certainly makes the emotional meltdown of coddled 20 and 30-something journalists, who seriously claimed that they were “endangered” by a U.S. Senator’s NYT column advocating for a military presence to maintain order in cities, look especially disconnected and bizarre. So one could understand why the media would be reluctant to feature the “voices” of minorities who take an alternate view.
There’s also the barely-hidden fear that properly depicting the after-effects of these riots would somehow “help Trump” during an election year. Even if it could be established as true that reporting on a historically significant event would “help” the incumbent president, refraining from such reportage on that ground would obviously be wildly improper from a journalistic perspective.
But even from a raw political standpoint, it’s almost certainly not even true. Trump’s inability to convert this post-riot political environment into some kind of electoral advantage is an irony unto itself, given the theme of his inaugural address — which ominously (but not entirely unjustifiably) invoked the specter of “American carnage”. For all the non-stop hysteria painting Trump as some kind of maniacal fascist, it truly is a lousy fascist who fails to leverage widespread social unrest and instability to consolidate power.
Needless to say, Trump is also currently presiding over a disastrous federal pandemic response, and rapidly shedding support among elderly voters. So if one insists on behaving purely as a partisan actor — which many contemporary journalists certainly are — any fatuous “would it help Trump?” calculation ought to be irrelevant.
Trump or no Trump, the lack of adequate coverage is the true affront. It should be more widely known that large swathes of a major American metropolis, Minneapolis/St. Paul, still lies in rubble over a month after the riots. And the main perpetrators of this destruction — namely those who committed the most incendiary arson attacks — were, by many accounts relayed to me directly, white Left-wing activists. Refusing to seek out and accurately present this information reflects the mainstream media’s propensity to operate under predetermined, politicised assumptions that are antithetical to any rightly-understood conception of journalism.
Travelling around Minneapolis, one frequently sees the anarchist “A” symbol scrawled on charred and/or boarded-up buildings, as well as catchphrases like “Viva La Revolucion” — expressions typical of Left-wing activists. Indeed, it’s abundantly clear that there was a strong ideological component to these riots, one that’s also been under-emphasised by the media, again likely because of the belief that it could in some vague sense “help Trump.” I spoke to numerous residents who are convinced that white out-of-towners were the ones who instigated the most severe chaos, after which locals latched on opportunistically. Marianne Robinson, a black woman who has resided in Chicago’s South Side for decades, asked me if I was familiar with “antifa” and blamed them for the riots.
Flora Westbrooks of Minneapolis, whose hair salon was burned down, was likewise convinced that the perpetrators could not have possibly been familiar with the neighbourhood given her longstanding community ties there. The theory might be a tad over-simplistic, but it does seem at least partially accurate. A (white) rioter I interviewed, who was present when the Third Police Precinct building in Minneapolis burned, remarked to me that he found himself in jail alongside people who came from as far as Missouri, Florida, Colorado, California and other distant states. He said they ventured to Minnesota out of a mixture of thrill-seeking and inchoate political grievance.
A police officer on foot patrol in Chicago’s heavily-black West Side remarked to me how perplexed she was by the lack of coverage of the damage in these neighbourhoods. Indeed, a simple drive around such parts of Chicago reveals a stunning number of boarded-up establishments, many of which appear like they will never return. The officer mused that she enjoyed the social-work aspects of the job — I watched her greeting various street-dwellers by name — and so, far from seeing the “Defund the Police” slogan and other expressions of animosity as an existential threat to the Chicago Police Department, regarded it as so detached from her everyday experience that she wasn’t even bothered. Over the course of my ten days in Minneapolis, I didn’t see a single officer on foot patrol, which is highly unusual for a major American city.
In Chicago, at the peak of the riots during the last weekend in May, there were a record-breaking 18 homicides in a single 24-hour period — the most since such data started being collected in 1961. I mention this not to make a knee-jerk “what about black-on-black crime” point, but simply to ask in general terms: why wasn’t this historic occurrence featured more prominently in the coverage of these protests?
Something extreme just happened in America. I could give dozens of additional examples of reportorial tidbits which don’t align with the prevailing media narrative that has flourished in the wake of this “movement”. And if you hadn’t seen it directly, would you ever know?








Join the discussion
Join like minded readers that support our journalism by becoming a paid subscriber
To join the discussion in the comments, become a paid subscriber.
Join like minded readers that support our journalism, read unlimited articles and enjoy other subscriber-only benefits.
Subscribe