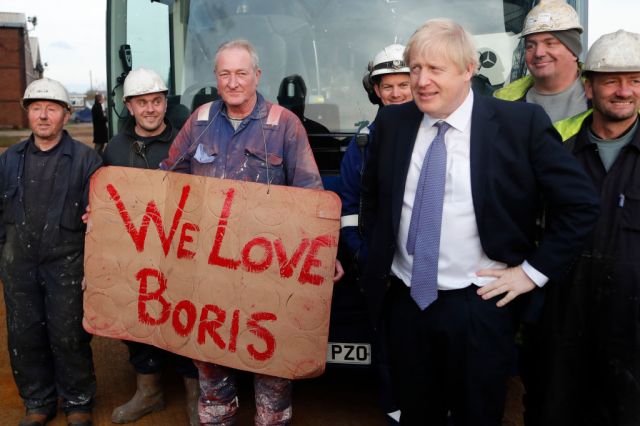
Boris Johnson campaigns in what was the Red Wall. Credit: Frank Augstein – WPA Pool/Getty Images

Do you remember Mods versus Rockers? No, not the original clash between rival youth cultures in the 1960s, but another infamous punch-up: the Tory Wars of the early 2000s, in which the Mods and Rockers were rival factions of the Conservative Party.
The Mods were the Modernisers — reformists who wanted to ‘detoxify’ the Tory ‘brand’. They talked like a bunch of PR consultants, because that’s what a lot of them were. They saw themselves as forward-looking, sophisticated and socially liberal. Unlike the old Tory ‘Wets’ they were economically liberal too and moderately Eurosceptic (but minus the Thatcheresque baggage). Their message to the party was change or die.
They were opposed by the Rockers (also known as the Headbangers), who thought that change was death — a betrayal of everything that real Conservatives stood for.
The split wasn’t without its complications. There were those, like William Hague (Tory leader from 1997 to 2001) who tried to straddle the divide. However, the messiness of the compromises only increased the bitterness of the conflict.
At the time, I was a very junior apparatchik working in Conservative Central Office. During the 2001 leadership contest, I remember the partisans of Michael Portillo — the candidate of the Mods — striding around the building as if they already owned the place. Staffers were quizzed as to their loyalties and with a smile I told them I’d be “voting for Michael” — the joke being that the only person standing against Portillo at the time was the party chairman and Hague loyalist, Michael Ancram.
In the event, neither of the Michaels would become leader; instead, the crown went to Iain Duncan Smith, who back then was the Rockers’ Rocker. That set off a further round of Tory Wars, followed by a truce under a third Michael (Michael Howard) and finally the ascent of David Cameron.
By that time, and with the scent of power once more in Tory nostrils, the whole Mods versus Rockers thing was burning out. The factions parked their scooters and motorbikes and looked forward to their ministerial cars. In any case a new divide was beginning to open up — Leave versus Remain — and, as we know, that would change everything.
And yet there’s one aspect of the old conflict that still persists. It’s about how to build an election-winning coalition. The true blue Tory heartlands aren’t enough on their own. To get from second place to first, the Conservatives need to reach out to another section of the electorate. But which one? For the Mods the answer was always obvious — people rather like themselves: young(ish), university-educated professionals. The Rockers wanted an alternative coalition, but as to what it might be they had no convincing answer — which is why they lost their war with the Mods.
However, in the 2016 Brexit referendum and the 2019 general election, Dominic Cummings, Boris Johnson and Michael Gove (all former Mods, ironically) cracked the problem. They forged an alliance not between the Tory Shires and Cool Britannia, but between the Tory Shires and the Red Wall — the supposedly uncool towns and suburbs of Northern England, the Midlands and Wales.
Daniel Finkelstein — associate editor of The Times and Peer of the realm — is a Mod grandee. He was a senior advisor to William Hague and David Cameron and, among many other contributions, wrote their best lines.
Last week, he used his Times column to attack the un-Moddishness of the Government’s political and economic strategy. This is the policy of “levelling-up” — i.e. pumping investment into left-behind parts of the country to achieve a lasting realignment of wealth, power and party loyalties. Can it succeed? Finkelstein has his doubts:
“The supposed political dividend for the Tories is that it will enable them to win and retain support among older, less prosperous, less well educated (note: not less intelligent, just less well educated) and more culturally conservative voters.
“I have always questioned whether this strategy is sustainable in the long run.”
Well, let’s make some long run comparisons between the Cameron era and what followed. In both 2010 and 2015, David Cameron and George Osborne went with the Mod strategy of appealing to younger, more prosperous, well educated and culturally progressive voters. Up to a point, they succeeded. In 2010, they increased the Tory vote share from 32.4% to 36.1%. In 2015, they pushed it up a bit further to 36.9%. Not too bad, but a long way from breaking through the 40% barrier.
It was Theresa May who managed that — getting 42.4% of the vote in 2017. Two years later, Boris Johnson pushed the share even higher to 43.6%. Add in the Brexit referendum as well — and it seems obvious to me that the Moderniser’s coalition is significantly smaller than the populist alternative.
Of course, in many ways the snap election of 2017 was a fiasco. While the blame for the Conservative campaign has been pinned on Nick Timothy alone, the fact is that it was disastrously conceived and executed in almost every respect. And yet despite the omnishambles, the Tory vote share still soared to levels not seen since 1992 — a stress test of the soundness of the underlying strategy.
The competent but uninspiring campaign of 2019 provided further confirmation — delivering a majority of 80 and a stunning gain of 50 seats across the Red Wall regions.
OK, that’s the politics, but what about the economic sustainability of the populist path? Can the levelling-up agenda really deliver the jobs and prosperity that the Conservatives have promised to their new supporters?
Finkelstein’s core criticism is that the people who create prosperity are not those who the Government is trying to appeal to. Therefore the Government’s approach is fundamentally incoherent:
“Social liberalism and economic prosperity go together. Whatever the political pros and cons of combining levelling up with an attack on metropolitan values, I don’t think it will work economically.”
Indeed, “in order to match the success and power of metropolitan areas, non-metropolitan places need to become more . . . metropolitan.”
It’s a thought-provoking argument, but is it a sound one? It strikes me that it rests on three basic assumptions. Firstly, that there is indeed a ‘Creative Class’ whose presence is the vital determinant of whether an area is successful or not. Secondly, that left-behind areas can only become more successful if they become more metropolitan. And thirdly, that the values of either the Government or left-behind Britain are so culturally conservative as to have a negative impact on the economy.
Let’s have a look at each of these in turn.
Firstly, the concept of a crucially important Creative Class.
Finkelstein gets this from the theories of Richard Florida, an American academic. The Creative Class are the artists, innovators, entrepreneurs and other ground breakers who pioneer the regeneration of up-and-coming neighbourhoods, start up new businesses and generate the excitement on which economic revival depends. These are the agents of change and if you can lure them to your community, then all sorts of other good stuff will follow. Or, as Finkelstein puts it:
“To be successful, places need to attract and keep members of this creative class. Florida suggests one way to do this is to improve night life, cultural attractions and a reputation for tolerance and diversity.”
Nice theory, but is it true? Finkelstein mentions one sceptic — Edward Glaeser — who points out that cities cannot live on cool alone and also have to attend to the dull stuff because “creative people have children too”. Glaeser’s critique goes rather further than that, however.
He crunches the numbers and finds that if the creative class is narrowly defined — i.e. the authentic arty-farty types — then, no, it doesn’t make much difference to economic outcomes. Yes, the trendsetters are, by definition, the first to move into an up-and-coming area. But that doesn’t mean they’re the reason it’s up-and-coming. They’re like the robins and blackbirds who show up when a garden is dug and planted. Perfectly charming, but it wasn’t them who turned the sod.
This is why using public money to build the sort of buildings that boring people think might be attractive to interesting people doesn’t work. Funding committees do love an ugly shed filled with second-tier modern art and less-than-compelling museum exhibits, but theirs is the logic of the cargo cult. Even if the attractions weren’t so unattractive, the understanding of the cause-and-effect is completely wrong. Bureaucratic fiat won’t turn, say, the Black Country into the abode of hipsters — and even if it could, it wouldn’t be much help.
But about the wider Creative Class? On a broader definition, Finkelstein suggests that it could include up to 40% of the population. But at such a large proportion of the workforce, the description loses all meaning — it’s just a fancy label for anyone with skills that command an above average salary. This group is associated with economic productivity, but they wouldn’t get paid what they do if they weren’t.
What makes them productive? Well, with all due respect, it isn’t just down to their innate talents. They are the beneficiaries of an education system that privileges academic over technical qualifications. They live in parts of the country — especially London — that get the lion’s share of public spending on research and infrastructure. And they work in sectors that have been favoured by long-term government policies at the expense of other sectors. For instance, a tax regime that sucks foreign capital into the UK property market and other speculative bubbles is good for landowners and the financial sector, but, thanks to the impact on exchange rates, bad for manufacturers and other exporters.
As for left-behind communities needing to become more metropolitan, the fact is that many of them are metropolitan. This is one of the most urban countries in the world. Beyond our capital, seven of the eight biggest cities in England are in the Midlands and the North.
There’s nothing undiverse about Manchester, Liverpool, Leeds, Sheffield, Nottingham, Newcastle and Birmingham. Their streets are full of sounds, sights and tastes from all around the world. These are university cities too — with big student populations and the nightlife and radical politics to match.
And yet set against comparable cities in France and Germany, there’s a long record of these communities underperforming economically against the national average. That’s not because they’re insufficiently metropolitan, but because they’ve been systematically starved of power and resources. Just look at the ramshackle transport links within and between Liverpool, Manchester, Leeds and Sheffield. Collectively, these cities and their wider city regions form one of the great conurbations of the world. Indeed, as the birthplace of the Industrial Revolution, this is where the modern world came into being. We should regard it as a great national asset, but instead its been marginalised.
One of the best things that Cameron and Osborne ever did was to recognise the potential of the Northern Powerhouse — and to start returning resources and decision-making power to its city-regions. But to keep this progress going in the right direction is a constant battle — Whitehall resistance to the creation of a powerful Transport for the North being a case in point.
Or consider the split between central and local government spending over the last 25 years. Tom Forth shows us that of the five biggest European economies, Britain is the only one where the share of GDP spent by central government has grown, while that spent by local government has shrunk. Whether or not one believes that left-behind Britain needs to become more metropolitan, it’s an unfortunate metropolis that can’t direct its own future.
But of course Daniel Finkelstein isn’t just talking about the places, but also the people — and, to his mind, left-behind Britain is lacking in the right sort. “The problem with the metropolitan ‘elite’ isn’t that there is too much of it”, he says, “it’s that there aren’t enough members of it, drawn from a wide enough background and living in enough places.”
If by ‘elite’ he means graduates, then we produce lots of those already — and from the most impressive line-up of universities of any county outside America. Where Britain is at a clear disadvantage, however, is in intermediate skills — i.e. those that provide the best opportunities for the non-graduate population. As a 2016 report from the Centre for Cities shows, skills provision in Britain outside London and the South East is abysmal — comparable to the poorest parts of southern and eastern Europe.
That we went to such great lengths to expand our the university system while neglecting technical education is a national scandal. The current Government has indicated a long overdue change of direction, but why so many decades of neglect? It is because the metropolitan elite used their position of centralised control to invest in people like themselves — while sidelining everyone else.
It didn’t have to be this way. The imperatives of the knowledge economy could have been interpreted more inclusively. Other countries, like Germany and Switzerland, created technical systems that have have spread economic opportunity instead of concentrating it. We could have done the same, but chose not to.
A more even spread of investment in skills — and also infrastructure and R&D — would also encourage a more even spread of the graduate workforce, which is not in short supply, just overly bunched-up.
*
Finally, the question of values.
I don’t believe that showing a bit of respect for left-behind communities — their aspirations, their identities, their loyalties — constitutes an “attack on metropolitan values”.
Nor does it threaten economic development. Regional economies are geographically and sociologically complex. There are the urban centres, with their youthful, transient, bourgeois bohemian populations. And then there are the outer suburbs, smaller cities, outlying towns and countryside that are necessarily different in character. That doesn’t mean that they can’t coexist or don’t need one another or won’t share in the same prosperity. Economies thrive on diversity and that includes viewpoint diversity. After all, it works pretty well in London and the surrounding region. Edgy, achingly hip neighbourhoods like Dalston are just a short commute away from the Essex outskirts where a working class conservatism holds sway instead.
It was in seats like Romford and Upminster where the Conservative revival started back in early 2000s. At the time, with the Tory Wars still raging, I remember the Mods telling us to disregard these results — because such areas were not typical of the nation as a whole.
However, it turned out that they were a prototype for the leave-voting seats where Boris Johnson won his thumping majority last year. Essex showed that working class electorates will respond positively if they feel the Conservative Party respects their small-c conservative values and also cares about their economic well-being. Being linked into the engine of prosperity that is London, meant that it was easier for Essex Man and Woman to believe this.
Hundreds of miles from the capital, it took the voters of the Red Wall a lot longer to be convinced. The Conservatives had to prove themselves. Getting Brexit Done was the first part of the deal and, now, levelling-up is the second.
These new Tory voters just want the same opportunities as their southern counterparts. And there’s no reason why they shouldn’t have them. What already works in London and the South East can work elsewhere — and to everyone’s benefit.








Join the discussion
Join like minded readers that support our journalism by becoming a paid subscriber
To join the discussion in the comments, become a paid subscriber.
Join like minded readers that support our journalism, read unlimited articles and enjoy other subscriber-only benefits.
Subscribe