The scandal of Johnny & Associates, the talent agency which supplied Japan’s light entertainment TV shows with photogenic and very young male pop stars, has rumbled on this year. Here, the country has at last been able to observe the culture of sexual abuse at Japan’s most famous dream factory under the leadership of its predatory eponymous founder, Johnny Kitagawa. The company, since renamed Smile-Up, is in the process of paying compensation to the estimated 800 victims.
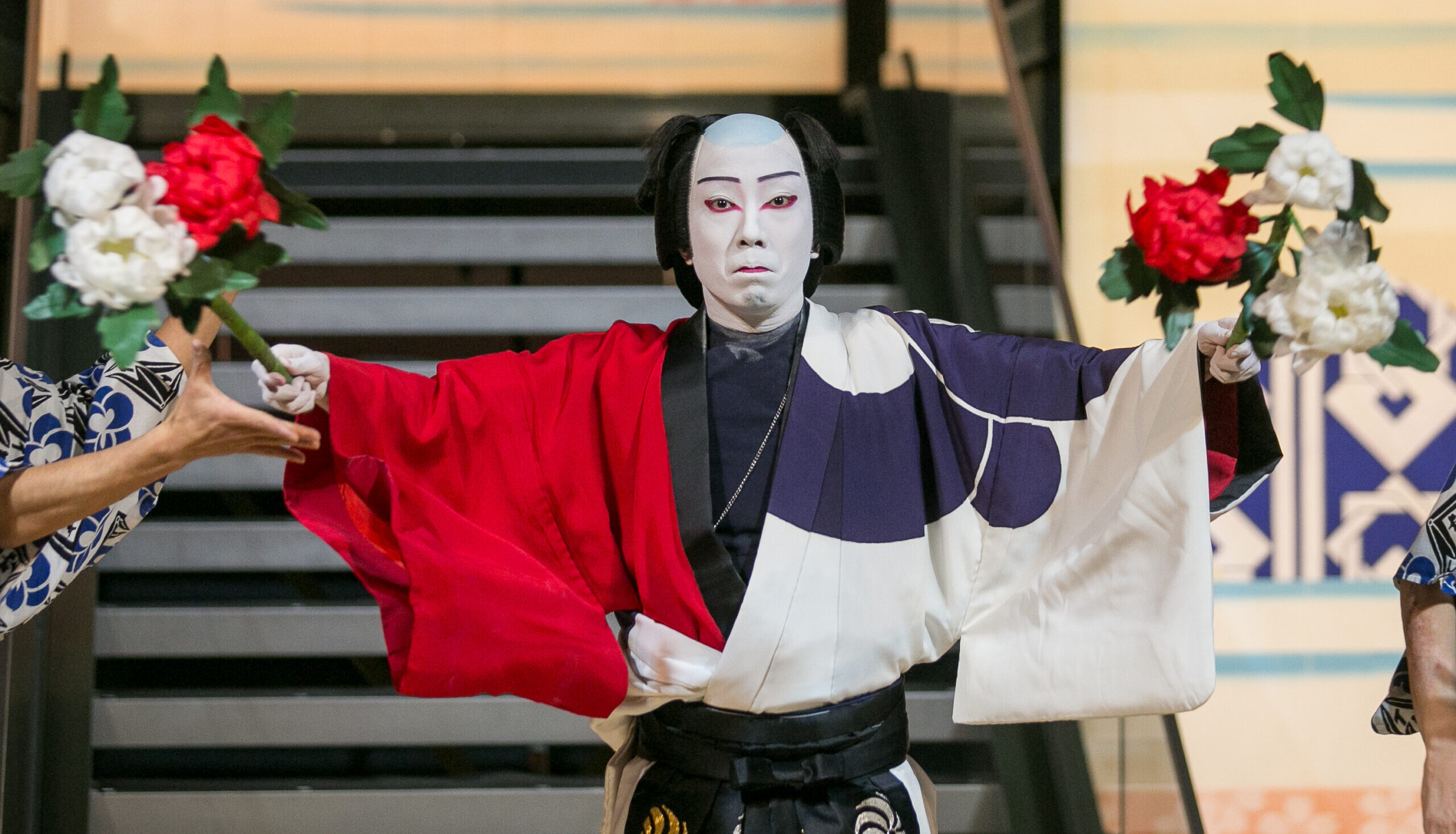
Since then, the scandal has metastasised, with allegations of psychological and sexual abuse made across the Japanese entertainment industry. The most bizarre story of all has been the alleged suicide pact involving well-known kabuki actor Ichikawa Ennosuke and his elderly parents. This was apparently prompted by sexual harassment allegations the star expected would be made against him in a weekly magazine. Ennosuke’s parents were found dead while he survived, and he received a three-year suspended sentence last month for assisting in their deaths.
Then the all-female Takarazuka Revue theatre company, which stages syrupy Andrew Lloyd Webber-style versions of classic operas and is known for its military-level discipline, was rocked by the death, ruled most likely a suicide by police, of one of its young actresses. The girl’s parents have alleged that “overwork and power harassment” led to her death. Kenshi Koba, the chairman of the Revue, resigned last month, acknowledging a “strong psychological burden” placed on the young woman and the company’s failure to “fulfil its duty of care”.
That last admission is telling. A generation ago, the idea that a theatre company in Japan had “a duty of care” beyond the most basic health and safety requirements would have been lost in translation. Japanese working culture was defined by a strict hierarchy, with a clearly defined senpai (senior)/ kohai (junior) division that governed everything from who pours the drinks at after-work parties to the language used between staff.
The MeToo movement had some influence in Japan in exposing the excesses and dangers of this system, but the first cracks probably appeared much earlier with the sumo scandal of 2008. Japan’s traditional sport was hugely damaged by allegations of serious physical abuse of young wrestlers by their trainers and senior stablemates. Accompanied as this was by allegations of yakuza involvement and match fixing, it presaged the darkest period in the sport’s millennia-long history, from which it has yet to fully recover.
Japan, economically and geopolitically weak, now feels increasingly inclined to submit to “gaiatsu” (outside pressure), including high-profile movements like MeToo. The BBC’s documentary about Johnny’s, Predator, caused a stir beyond Japan. Meanwhile, J- and K-pop are no longer marketed only for domestic consumption, but instead successfully seek out international audiences.
As for the future, the rebranding of Johnny’s has stoked fears that any changes will be purely cosmetic. But with major firms such as Nissan, Asahi, Kirin and Suntory cutting ties with the agency, and NHK (Japan’s BBC) declaring that it won’t use any of the company’s artists in its showpiece New Year singing contest, a watershed moment has seemingly been reached. Expect more revelations, more resignations, and a far greater focus on safeguarding and that “duty of care”. Whether such measures will extend beyond the world of showbiz and into Japan’s humdrum offices, where sexual harassment is rife, is less certain.









Join the discussion
Join like minded readers that support our journalism by becoming a paid subscriber
To join the discussion in the comments, become a paid subscriber.
Join like minded readers that support our journalism, read unlimited articles and enjoy other subscriber-only benefits.
Subscribe